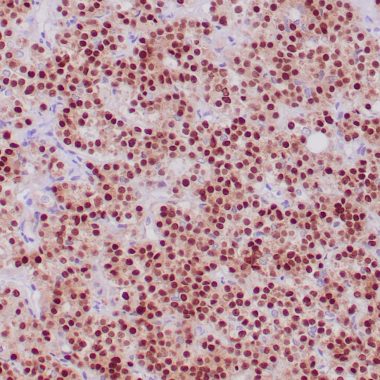
Transcriptional regulators play a critical role in development by mediating tissue- and cell-specific transcription. POU domain factors are transcriptional regulators characterized by a bipartite DNA binding domain consisting of two highly conserved regions, tethered by a variable linker of 14-26 amino acids. Pit-1, also known as growth hormone factor-1 (GHF-1), a member of the POU homeodomain family, is essential for the normal development of the anterior pituitary gland, where it is required to form of somatotropes, lactotropes, and thyrotropes. In somatotropes and lactotropes, Pit-1 activates the production of growth hormone and prolactin, respectively. In addition, Pit-1 acts as a repressor of gene expression, which allows for the differentiation of specific cell types. Pit-1 is expressed as two alternatively spliced products, designated Pit-1a and Pit-1b, which differ in their trans-activation ability. Mutations in the Pit-1 gene are believed to result in combined pituitary hormone deficiency (CPHD) for growth hormone, Prolactin, and thyroid-stimulating hormone. The gene which encodes Pit-1 maps to human chromosome 3p11.2.