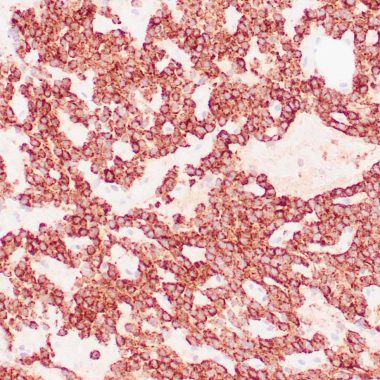
Human parathyroid gland stained with anti-PTH antibody using peroxidase conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining in glandular cells.
Related Products
PTH is produced in the parathyroid gland as an 84 amino acid single chain polypeptide. It can also be secreted as N-terminal truncated fragments or C-terminal fragments after intracellular degradation, as in case of hypercalcemia. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH); also called autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism or autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. FIH is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia due to inadequate secretion of parathyroid hormone. Symptoms are seizures, tetany and cramps. FIH exist both as autosomal dominant and recessive forms of hypoparathyroidism.
Specifications
Species Reactivity:Humans; others not tested
Known Applications:Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
Supplied As:Buffer with protein carrier and preservative
Storage:Store at 2ºC to 8ºC
Control:Parathyroid
Visualization:Cytoplasmic
Isotype:IgG2b /κ
Immunogen:A synthetic peptide around aa 1-34 of human mature-PTH-polypeptide; A recombinant fragment around aa 32-115 of human mature PTH-polypeptide (exact sequence is proprietary)
Ordering Information
Package Inserts
IFU-Parathyroid hormone (PTH) ZM207
SDS