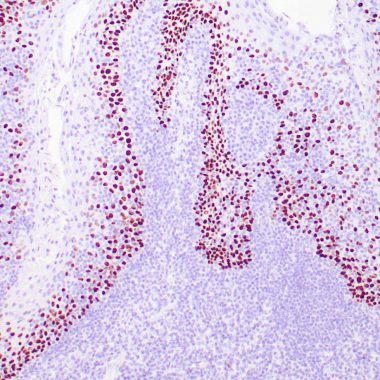
p63 consists of two major isoforms-TAp63 and DNp63. These isoforms differ in the structure of the N-terminal domains. The TAp63 isoform (identified by anti-p63 antibody) contains a transactivation-competent ‘TA’ domain with homology to p53, which regulates the expression of the growth-inhibitory genes. In contrast, DNp63 isoform (identified by anti-p40 antibody) contains an alternative transcriptionally-inactive ‘DN’ domain, which antagonizes the activity of TAp63 and p53. The p40 (clone ZR8) antibody recognizes exclusively DNp63 but not TAp63. p40 is a squamous cell carcinoma ‘specific’ antibody. It reacts with the vast majority of cases of squamous cell carcinomas of various origins, but not with adenocarcinomas. It is particularly useful in differentiating lung squamous cell carcinoma from lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. p40 antibody can also be used as an alternative basal cell/myoepithelial cell marker, which has similar sensitivity and specificity as that of p63 antibody. Therefore, p40 antibody may also be used as an alternative immunohistochemical marker for determining prostate adenocarcinoma vs. benign prostate glands and for determining breast intraductal carcinoma vs. invasive breast ductal carcinoma.