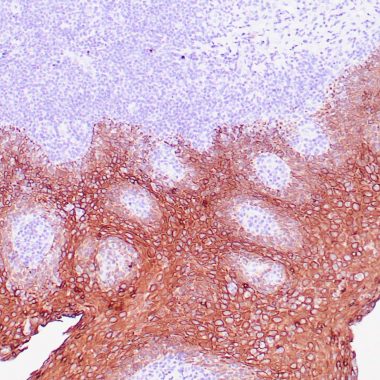
T+P112his MAb recognizes a protein of 58kDa, which is identified as Cytokeratin 5 (KRT5). This type II cytokeratin is specifically expressed in the basal layer of the epidermis with family member KRT14. Mutations KRT5 have been shown to result in the autosomal dominant disorder epidermolysis bullosa (EB). Cytokeratins comprise a diverse group of intermediate filament proteins (IFPs) that are expressed as pairs in both keratinized and non-keratinized epithelial tissue. Cytokeratins play a critical role in differentiation and tissue specialization and function to maintain the overall structural integrity of epithelial cells. Cytokeratins have been found to be useful markers of tissue differentiation, which is directly applicable to the characterization of malignant tumors.