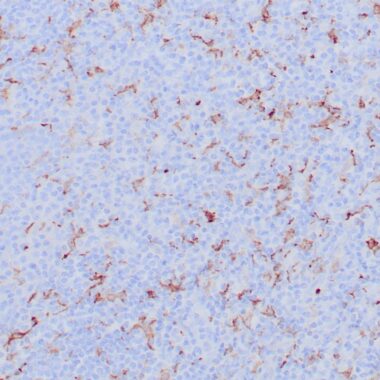
This MAb recognizes a protein of 140kDa, identified as CD163. It has been identified as an acute phase-regulated transmembrane protein whose function is to mediate the endocytosis of haptoglobin-hemoglobin complexes. This receptor is expressed on the surface of monocytes with low expression and on tissue macrophages, histiocytes with high expression. Staining with anti-CD163 has been helpful to distinguish synovial macrophages from synovial intimal fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis, where its specificity for macrophages was found to be superior to that of anti-CD68. Increased levels of CD163 were also detected in patients with microbial infections and myelomonocytic leukemias. Anti-CD163 is of considerable value for selective identification of monocytes and macrophages at a certain stage of differentiation and is suitable for diagnosing myelomonocytic or monocytic leukaemia and neoplasms of true histiocytic origin. CD163 is positive in skin (histiocytes), gut, Kupffer cells, a few alveolar macrophages, macrophages in the placenta, and in macrophages in inflamed tissues including tumor tissue.