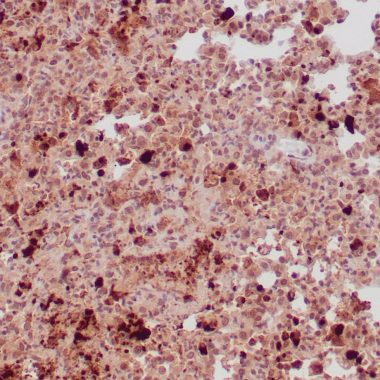
Human lung infected with toxoplasma gondii stained with anti-toxoplasma gondii antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note positive staining of organisms..
Toxoplasma gondii, a single-celled parasite, causes the disease toxoplasmosis. The life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii includes two phases: the intestinal (or enteroepithelial) and extraintestinal phases. The intestinal phase produces oocysts and occurs only in wild and domesticated cats. The extra-intestinal phase occurs in all infected animals and produces tachyzoites (actively proliferating trophozoites) and, eventually, bradyzoites (slowly growing trophozoites) or zoitocysts. Toxoplasma gondii infects tissue of the gastrointestinal tract, brain and lung in immunocompromised patients.
Specifications
Species Reactivity:Humans; others not tested
Known Applications:Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
Supplied As:Buffer with protein carrier and preservative
Storage:Store at 2ºC to 8ºC
Control:Toxoplasma Gondii infected tissue
Visualization:Organisms
Isotype:IgG
Immunogen:Toxoplasma gondii
Ordering Information
Package Inserts
IFU-Toxoplasma gondii Poly - RUO
SDS