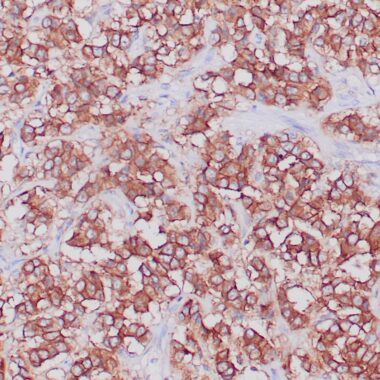
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human neuroendocrine tumor stained with anti-SSTR2 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells
Related Products
SSTRs (for somatostatin receptors) represent a family of G protein-coupled receptors which mediate the diverse biological actions of somatostatin (SST). There are five distinct subtypes of SSTRs that bind two natural ligands, SST-14 and SST-28. SSTR2 gives rise to spliced variants, SSTR2A and 2B. SSTRs share common signaling pathways such as the ability to inhibit adenylyl cyclase via GTP binding proteins. Some of the subtypes are also coupled to tyrosine phosphatase (SSTR1,2), Ca2+ channels (SSTR2), Na+/H+ exchanger (SSTR1), PLA-2 (SSTR4), and MAP kinase (SSTR4). Individual target cells typically express more than one SSTR subtype and often all five isoforms. Subtypes of SSTR can form functional homo- and heterodimers.
Specifications
Species Reactivity:Humans; others not tested
Known Applications:Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
Supplied As:Buffer with protein carrier and preservative
Storage:Store at 2ºC to 8ºC
Control:Neuroendocrine tumor
Visualization:cell surface
Isotype:IgG
Immunogen:Recombinant fragment (around aa 169-369) of human SS2R
Ordering Information
Package Inserts
IFU-Somatostatin Receptor Type 2 (SSTR2) ZR233- 0
SDS