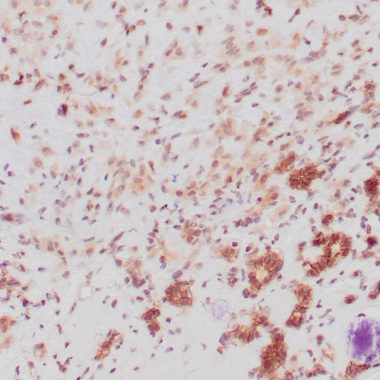
Alpha-catenin and beta-catenin bind to the intracellular domain of E-cadherin while p120 catenin binds E-cadherin at a juxta-membrane site. The complex stabilizes tight junctions. In the cell, p120 catenin localized to the E-cadherin/catenins cell adhesion complex directly associates with cytoplasmic C-terminus of E-cadherin and may similarly interact with other cadherins. p120 is a proliferation-associated nucleolar protein found in most human malignant tumors, but not in resting normal cells. In colorectal cancer, the altered localization of p120 catenin corresponds with a loss of cytoplasmic localization of E-cadherin. Studies have shown accurate categorization of ductal vs. lobular neoplasia in the breast was achieved with p120 staining. p120 expression further clarifies the separation of low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ from lobular neoplasia. Studies also have shown that altered expression of p120 catenin antibody predicts poor outcome in invasive breast cancer.