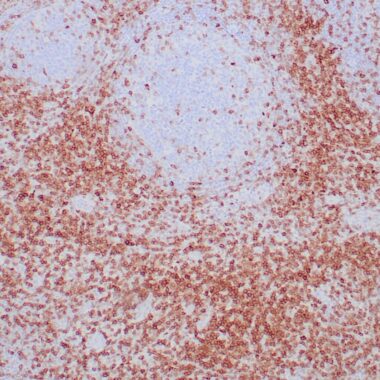
Recognizes a protein of 40kDa, identified as CD7 (also known as gp40, Leu9). CD7 is a member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Its N-terminal amino acids 1-107 are highly homologous to Ig kappa-L chains whereas the carboxyl-terminal region of the extracellular domain is proline-rich and has been postulated to form a stalk from which the Ig domain projects. CD7 is expressed on the majority of immature and mature T-lymphocytes, and T cell leukemia. It is also found on natural killer cells, a small subpopulation of normal B cells and on malignant B cells. Cross-linking surface CD7 positively modulates T cell and NK cell activity as measured by calcium fluxes, expression of adhesion molecules, cytokine secretion and proliferation. CD7 associates directly with phosphoinositol 3′-kinase. CD7 ligation induces production of D-3 phosphoinositides and tyrosine phosphorylation.