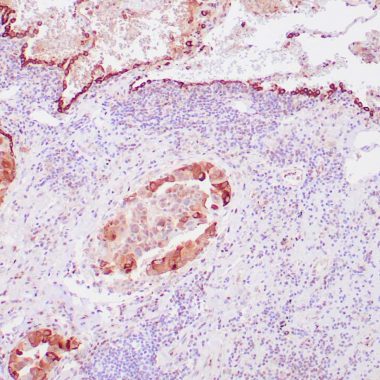
Pulmonary surfactant is primarily responsible for lowering the surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the alveoli, a process that is essential for normal respiration. Pulmonary surfactant is a mixture of phospholipids and proteins, including four distinct surfactant-associated proteins (SPs), SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, SP-D. SP-B and SP-C are predominantly hydrophobic proteins that associate with lipids to promote the absorption of surfactant phospholipids and to reduce the surface tension in the alveoli. SP-A and SP-D are large multimeric proteins belonging to the family of calcium-dependent lectins, designated Collectins, which contribute to the innate immune system. Both SP-A and SP-D have been shown to protect against microbial challenge through binding to the lipid components of the bacterial cell wall and facilitating the rapid removal of microbials.