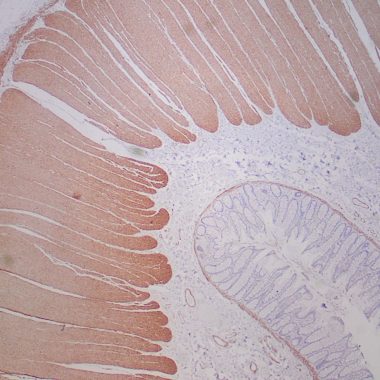
Smoothelin is found exclusively in contractile smooth muscle cells. It associates with stress fibers and constitutes part of the cytoskeleton. Smoothelin expression is limited to large veins and arteries capable of pulsatile contraction in the vascular system. As a marker for the highly differentiated contractile smooth muscle cell, smoothelin expression helps study vascular malformation and injury. It is a constituent of the smooth muscle cell cytoskeleton protein exclusively found in differentiated smooth muscle cells (SMC). Cells with SMC-like characteristics, such as myofibroblasts and myoepithelial cells, and skeletal and cardiac muscle do not contain smoothelin. Distinguishing bladder muscularis mucosae (MM) from muscularis propria (MP) muscle bundles is crucial for accurate staging of bladder carcinoma. Strong smoothelin expression is nearly exclusively observed in muscularis propria. Therefore, the staining pattern of MP (strongly positive) and MM (negative or weakly positive) makes this antibody an attractive diagnostic tool. Anti-smoothelin immunostaining can be helpful in differentiating benign (+) from malignant smooth muscle tumors (-) and other mimics (-).