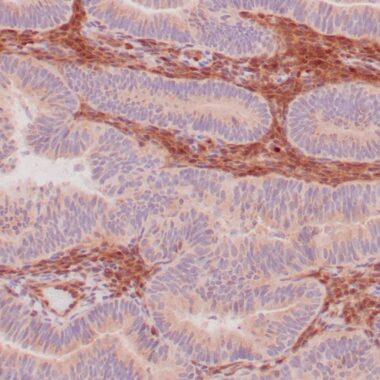
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human endometrioid adenocarcinoma stained with anti-PTEN using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note carcinoma is negative whereas stromal cells are positive
PTEN (phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase) contains a tensin-like domain as well as a catalytic domain similar to that of the dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases. It was identified as a tumor suppressor that is mutated in a large number of cancers, including sporadic brain, breast, endometrial, kidney, and prostate cancers.
Specifications
Species Reactivity:Humans; others not tested
Known Applications:Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
Supplied As:Buffer with protein carrier and preservative
Storage:Store at 2ºC to 8ºC
Control:Endometrial adenocarcinoma
Visualization:Cytoplasmic and nuclear
Isotype:IgG
Immunogen:Recombinant full-length human PTEN protein
Ordering Information
Package Inserts
IFU-PTEN ZR235 - IVD 0
SDS