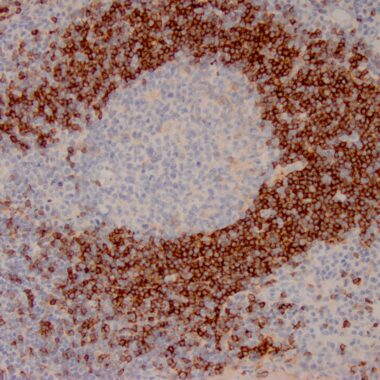
Immunoglobulins are four-chain, Y-shaped, monomeric structures comprised of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains held together through interchain disulfide bonds. The chains form two domains, the Fab (antigen binding) fragment, and the Fc (constant) fragment. Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is a monomer with δ heavy chains and either κ or λ light chains. It plays a biological role as a transmembrane receptor molecule, co-expressed with IgM on the surface of mature/naive B cells. In particular, it is found on spleen B cell surfaces. Compared to IgM, IgD exists in much lower numbers and is not expressed in immature B cells. IgD surface expression on B cells is regulated in part by IL-27. In mice, the inhibition of this immunoglobulin isotype does not cause a significant change to the immune system.