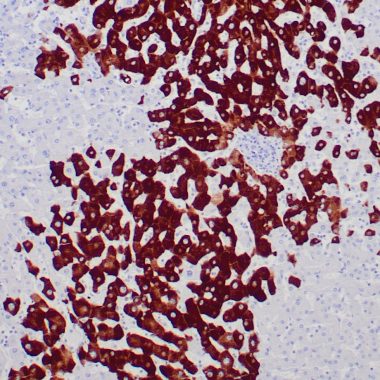
Human liver infected by hepatitis B virus stained with anti-HBsAg antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of infected hepatocytes.
Related Products
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is a glycoprotein on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. After hepatitis B infection, HBsAg appears as the first viral marker. HBsAg can be detected in blood, saliva, breast milk, sweat, tears, nasopharyngeal secretions, semen, and vaginal secretions of patients 2 to 6 months after infection with HBV. HBsAg antibodies are mainly used for the diagnosis of the hepatitis B virus.
Specifications
Species Reactivity:Humans; others not tested
Known Applications:Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
Supplied As:Buffer with protein carrier and preservative
Storage:Store at 2ºC to 8ºC
Control:Hepatitis B infected liver
Visualization:Cytoplasmic
Isotype:IgG
Immunogen:Recombinant full-length HBsAg protein
Ordering Information
Package Inserts
SDS