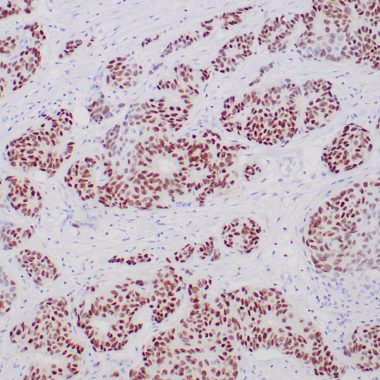
Estrogen receptor (ER) belongs to the steroid receptor superfamily of nuclear receptors. It is a protein with 553 amino acids. The receptor molecule has three domains, i.e., the central DNA-binding domain, the hormone-binding domain at the C-terminal, and the transcription-activating domain at the N-terminal. ER mediates regulatory functions of female sex steroids, mainly 17 (E2), on growth, differentiation, and function in several target tissues, including the female and male reproductive tract, mammary gland, and skeletal and cardiovascular systems. Studies have shown ER α is present in the nuclei of epithelial cells in normal breast and endometrial tissues and a subset of breast carcinomas. Studies with immunohistochemical assay show that positive steroid hormone status has predicted favorable overall survival, independently of hormonal treatment. Secondly, ER α can be used as a tumor marker, preferentially in combination with an antibody to the progesterone receptor, e.g., in the classification of adenocarcinomas.